How To Determine The Topic of Research In Education - When we as ordinary people (e.g., citizen), university students, business man/women, parents, teacher, athlete, doctor, police, military, etc sometimes has natural intuition or official obligation to inquire certain matter at some certain situation.
The term inquiry can be as same as the term of scientific research but also can be merely an ordinary investigation. In other words, not all inquiries are valuable at certain congregation (e.g., government, educational institutions, companies, and etc), it depends on the purpose and how the ways of knowing. For example, the parents inquires their son disposition with some natural method (i.e., they mark a reception pattern of son's behavior towards their certain treatment) to determine one or more veritable handling for their son—this inquiry using sensory experience in context of internal concern—hence this inquiry merely an ordinary investigation. However, there are many ways to obtain information such several types of ways of knowing which based on Fraenkel Jack R. (2009:4) bellow;
1. Sensory Experience
The term inquiry can be as same as the term of scientific research but also can be merely an ordinary investigation. In other words, not all inquiries are valuable at certain congregation (e.g., government, educational institutions, companies, and etc), it depends on the purpose and how the ways of knowing. For example, the parents inquires their son disposition with some natural method (i.e., they mark a reception pattern of son's behavior towards their certain treatment) to determine one or more veritable handling for their son—this inquiry using sensory experience in context of internal concern—hence this inquiry merely an ordinary investigation. However, there are many ways to obtain information such several types of ways of knowing which based on Fraenkel Jack R. (2009:4) bellow;
1. Sensory Experience
2. Agreement With Others
Agreement with other means the transmission of one person's information to the other person in order to obtain authenticity of its information. For instance, one person was hearing sound of the bell, and then ask other person whether he/she heard it too in order to acquire the authenticity of the information. This is also the same as the aforementioned above that the information contained in each person might be unreliable, however, someone's information might be wrong.
3. Expert Opinion
Expert opinion means consultation about its information that someone has acquired to the person whom has competence and expertise in its field. Again, in one hand, the authenticity of the given information is also depend on aspect of the expert's background. (e.g., his/her achievement, qualification and etc)
4. Logic
Logic means the process of reflection between general information into the specific information in order to acquire the authentic fact. For instance;
Major premise : All human beings are mortal.
Minor premise : Sally is a human being.
Conclusion : Sally is mortal
This three statements above is called syllogism process. According to the remark of Fraenkel Jack R—said that "to assert the first statement (called the major premise), we need only generalize from our experience about the mortality of individuals. We have never experienced anyone who was not mortal, so we state that all human being are. The second statement (called the minor premise) is based entirely on sensory experience. We came in contact with Sally and classify her as a human being. We don't have to rely on our senses, then, to know that the third statement (called the conclusion) must be true. Logic tells us it is. As long as the first two statement are true, the third statement must be true." Concisely, this syllogism also might lead the inquirer into misinterpretations if there is one of the first or second statement is false.
5. Scientific Method
Scientific method in this discussion means a process of dealing with the acquired assumptions or called as hypothesis conducted with a careful and structured test. According to Fraenkel, Jack R. (2009:6) scientific method has general order or steps as follow:
1. Identifying a problem or question
2. Clarifying the problem
3. Determining the information needed and how to obtain it
4. Organizing the information
5. Interpreting the results
So which one above is correct to conduct a research? First, we must know exactly what is the research and its important. According to Creswell, John W (2012:3)—said that "research is a process of steps used to collect information to increase our understanding of a topic or issue." In one hand, according to Fraenkel, Jack R (2009:7)—said that "the term research can mean any sort of careful, systematic, patient study and investigation in some field of knowledge." Concisely, the characteristic or nature of research is a careful, systematic and patient steps to collect information in order to obtain understanding of its question contained in the topic or issue. Hence fundamentally, the five ways above are interconnected, in other words, a set to conduct a research.
Sometimes someone (e.g., undergraduate student at certain institution.) whom recently has official obligation to conduct a research usually figuring out how to acquire a title or topic of his/her research proposal. Strictly speaking, that is wrong way to go. As the aforementioned remark of Fraenkel Jack R. (2009:6) above—that the first general step is to identify a problem that concern you, something that you have passion to solve it that in accordance with your major—not a title. For instance, imagine researcher concern about certain students' behavior towards researcher instructional activity, and it was bothering because it is always occurring in your class. However, it means that researchers have expectation to improve the condition, question that researcher want to seek the answer; and solved or clean up what is caused the problem. So researcher need to identify and clarify what is actually the problem by designing the background of the problem beforehand (e.g., inform something that it might be involves certain issue that relate certain field of knowledge, for example, teacher or students' psychology.). Second, researcher requires to design a literature review which include reliable sources to reinforce your statement of the problem. Third, design the statement of problem in order to bring out the research questions and aims so ultimately researcher able to define precise term of the dependent and independent variable (i.e., the topic of research). However research question must be questionable, in other words, worth for research. And if researcher define the term that utilize manipulation of the sample and include numeric inquiry, the research design should use quantitative method, while if the term include narrative or detail description without manipulating sample, the researcher will use research design of qualitative method. Here the figure bellow based on Creswel John W (2012) as for illustration whether to qualitative or quantitative:
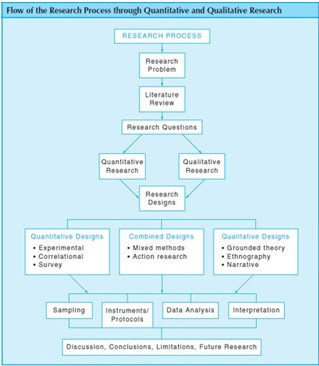 |
| Figure 1.2: Research Process |
Click like, if you satisfied
REFERENCE
Creswell, John W. 2012. Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research (4th edition). Boston, Massachusetts, USA: Pearson Education, Inc.
Fraenkel, Jack R., & Wallen, Norman E. 2009. How to design and evaluate research in education (7th edition). New York, USA: McGraw Hill Higher Education.
Related Post
Sign up here with your email
